引言
在具体讨论 KNN 算法之前,我们先通过一个具体的例子引入。我们创建一个数据集,并将其可视化出来。
1 | import numpy as np |
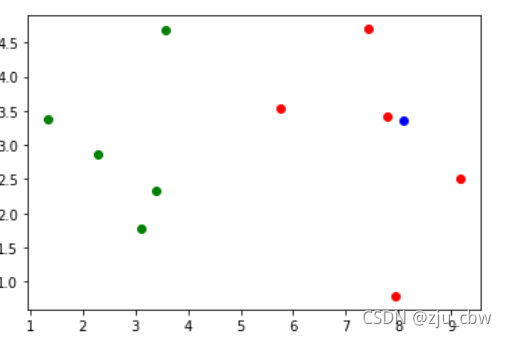
从上面的散点图中,蓝色的点明显更接近红色的点。我们将蓝色的点与其它点的距离求出来,并将最近的 5 个点选出来。
1 | from math import sqrt |
可以看到结果是 [1,1,1,1,1],如果我们将距离最近的 5 个点中,种类数量最多作为蓝色的点的种类,那么蓝色也就是归于红色一类,与我们之前看到的散点图一样。没错这就是 KNN 算法。
具体思想
KNN 即 K-Nearest Neighbors,其思想特别简单,就是设置一个超参数 k,对于一个新样本,我们计算其与所有训练集中数据的距离(这个计算距离的方式也可以选择,欧式距离、马氏距离….),然后选出最近的 k 个,进行投票,即 k 个数据中,类别最多的那一类即为新样本的类别。
是不是很简单,下面附一个手写的 KNN 解决手写数字识别的代码。
1 | import numpy as np |
超参数
我们已经知道,这个模型自己选择的部分一是 k 即选几个邻居,二是计算距离方法。但是实际操作中,可能会遇到平票的情况,而且只是通过类别的个数来判断有时也不是很准确,我们可以设定一个权重,一般为距离的倒数,这样离新样本越近的那个种类所具有的权重也越大,当然我们也可以自己根据具体情况自己设定计算权重的函数。
下面附一个,利用sklearn包的 KNN 分类器寻找最优超参数的代码。
1 | from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score |