简介
VGG是牛津大学的Visual Geometry Group的组提出的。该网络是在ILSVRC 2014上的相关工作(定位任务第一,分类任务第二),主要工作是证明了增加网络的深度能够在一定程度上影响网络的最终性能(对比了多个不同深度网络的性能)。
从上表可以发现,VGG只使用了两个网络就能获得非常好的效果。
主要方法
采用3x3卷积核
AlexNet采用了 11x11 7x7 5x5较大卷积核,而在VGG中,使用连续的 3x3 卷积核代替大卷积核,可以在保持感受野不变的情况下,减小参数量。
感受野计算
计算公式如下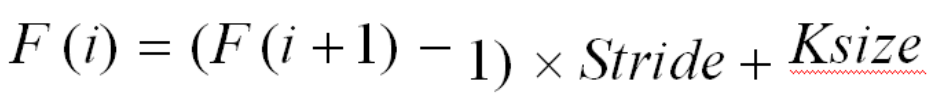
下面证明了为什么2个 3x3 的卷积核和1个 5x5 的卷积感受野一样
F(2) = 3
F(1) = (3-1)X1 + 3=5
而2个 3x3 的卷积核的参数量为 2X(9XC^2),1个 5x5 的卷积核的参数量为 25XC^2,C为输入和输出的通道数,并且层数会提高网络性能。
网络结构
除了A-LRN采用了LRN(发现并没有什么用),以及C采用了1x1卷积核,其它都只使用了3x3卷积核。
多尺度训练和测试
使用多个尺度训练与测试,可以提高网络的性能。
multi-crop evaluation与 dense evaluation
multi-crop evaluation就是裁剪为多个图片然后塞进网络进行测试,而dense evaluation是将最后的三层全连接层转化为全卷积层,这样可以接受所有尺度的图片。实验发现,这两种方法是互补的,因为他们关注的卷积边界情况不同,multi-crop为0填充,而dense为相邻像素填充。所以两者方法都使用会产生最好的结果。
参数初始化
除了A随机初始化参数,其它更深的网络使用了A网络第一个四个卷积层以及最后三个全连接的参数,随机初始化从零均值10^-2^方差的正态分布中采样获得,偏差初始化为0。并且发现使用Glorot and Bengio的初始化方法可以获得同样的效果。
Pytorch实现
从http://download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz下载数据集
执行下面代码,将数据集划分为训练集与验证集。
split_data.py
1 | import os |
model.py
1 | import torch.nn as nn |
train.py
VGG网络还是很大的,如果发现训不了,可以调小batch_size,或者使用cpu训练。
1 | import os |
predict.py
1 | import os |
Output: